🚨 Java Exception Handling - Interview-Friendly Guide
🧠 1. What is an Exception?
An exception is an event that disrupts the normal flow of a program at runtime. Think of it as a "warning light" that signals something went wrong, allowing the program to handle it gracefully instead of crashing.
🧠 Mnemonic for Interviews:
Exceptions are like "speed bumps" in your code. They slow down or stop execution unless you handle them properly!
🧃 Real-Life Analogy:
Imagine you're cooking:
- No ingredients left → EmptyPantryException: Order groceries.
- Pan overheats → OverheatException: Turn off the stove.
In Java, dividing by zero triggers an ArithmeticException that you handle similarly.
🧱 Code Example:
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
int result = a / b; // ❌ Throws ArithmeticException: divide by zero
🤔 Interactive Quiz for Interview Prep:
Q: What happens if an exception is not caught?
A: The program terminates, and the JVM prints the stack trace. Try running the above code to see!
🔺 2. Throwable Class & Exception Hierarchy
The Throwable class is the root of Java’s exception hierarchy. All exceptions and errors inherit from it, like the "trunk" of a family tree.
📦 Two Main Subclasses:
- Exception: Recoverable issues (e.g., file not found) – handle these!
- Error: Severe, unrecoverable problems (e.g., out of memory) – avoid catching!
🔍 Exception Hierarchy Diagram:
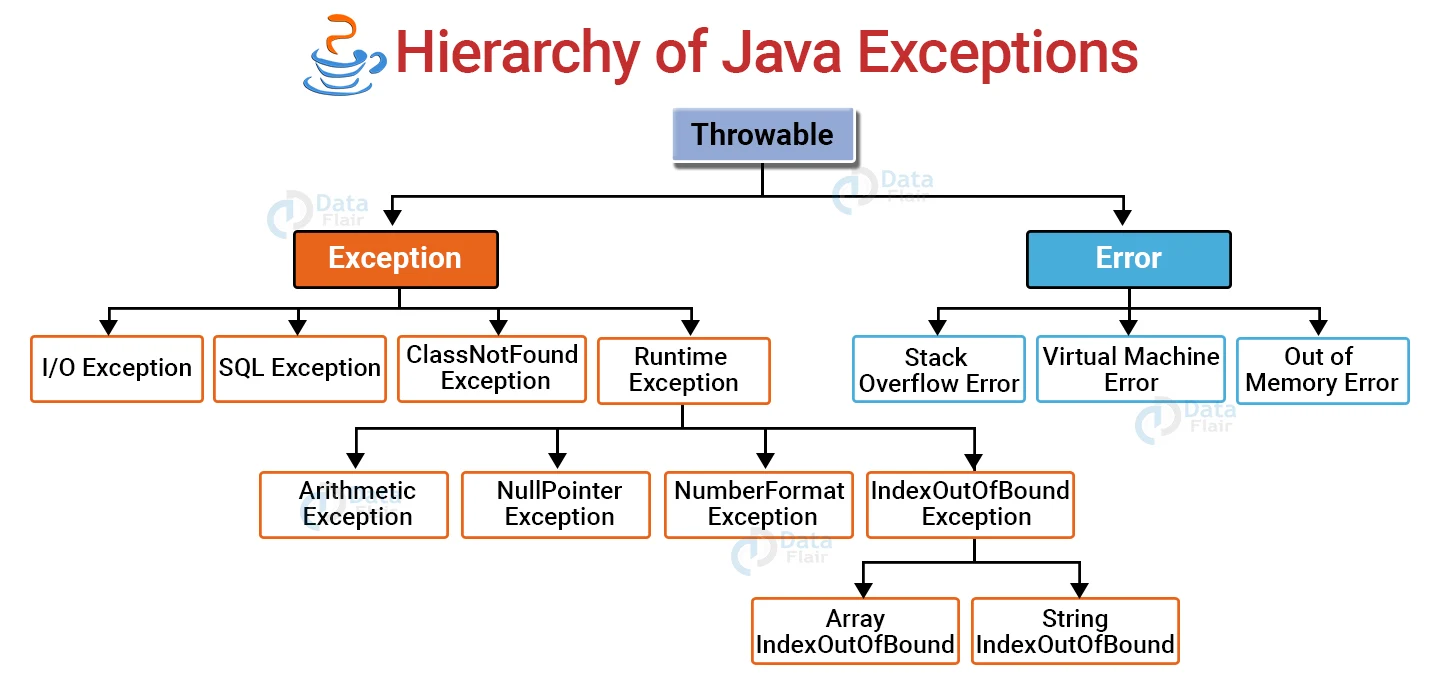
Fallback Text Diagram (if image fails):
Throwable
├── Exception
│ ├── Checked Exceptions (e.g., IOException, SQLException)
│ └── RuntimeException (Unchecked, e.g., NullPointerException)
└── Error (e.g., OutOfMemoryError, StackOverflowError)
✅ Checked Exceptions (Compile-Time)
🧠 Mnemonic: Checked exceptions are like "boarding passes" – you must show (handle/declare) them before compiling.
- Checked at compile time.
- Must be handled with
try-catchor declared withthrows. - Examples:
IOException,SQLException,FileNotFoundException.
⚠️ Unchecked Exceptions (Runtime)
🧠 Mnemonic: Unchecked exceptions are like "pop quizzes" – they surprise you at runtime.
- Occur at runtime, not checked by compiler.
- Optional to handle, but good practice to anticipate.
- Examples:
NullPointerException,ArithmeticException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
🚫 Error Class (Unrecoverable)
🧠 Mnemonic: Errors are like "server crashes" – too severe to fix in code.
StackOverflowError: Infinite recursion.OutOfMemoryError: No heap space.VirtualMachineError: JVM issues.
🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: Is IOException checked or unchecked?
A: Checked – must be handled or declared.
🧩 3. try-catch-finally
The backbone of exception handling: try for risky code, catch for handling errors, finally for cleanup.
🔧 Flow Diagram:

Fallback Text Diagram (if image fails):
[Start] → [Try: Risky Code]
├── Exception → [Catch: Handle It]
└── [Finally: Cleanup]
[End]
🔧 Syntax:
try {
// Risky code
} catch (ExceptionType e) {
// Handle exception
} finally {
// Cleanup (always runs)
}✅ Example:
try {
int result = 10 / 0; // Throws ArithmeticException
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Cannot divide by zero!");
} finally {
System.out.println("Cleanup done!");
}📝 Output:
Cannot divide by zero!
Cleanup done!
🧠 Mnemonic: Try = Test drive, Catch = Fix flat tire, Finally = Return car keys.
🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: Does finally execute if System.exit() is called?
A: No, it’s skipped on JVM shutdown.
🧪 4. throw vs throws
Key for controlling exceptions manually or warning about them.
🔍 Comparison Diagram:

Fallback Text Diagram (if image fails):
throw: Actively throws an exception object
throws: Declares possible exceptions in method signature
🧠 Easy Explanation:
throw: "I’m throwing this error now!" (Action).throws: "Heads up, this method might throw errors!" (Warning).
| Keyword | Meaning | Used In | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|
throw |
Manually throw | Method body | One at a time |
throws |
Declare | Method signature | Multiple |
✅ Throw Example:
void validateAge(int age) {
if (age < 18) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Underage!");
}
}✅ Throws Example:
void readFile() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("file.txt");
}🧠 Mnemonic: Throw = Toss the ball, Throws = Warn others to catch it.
🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: Can throws list unchecked exceptions?
A: Yes, but it’s optional since they’re not enforced by the compiler.
🏗 5. Custom Exception
Create tailored exceptions for specific scenarios, extending Exception (checked) or RuntimeException (unchecked).
🧠 Mnemonic: Custom exceptions are like "customized warning signs" for your app’s unique issues.
class InvalidAgeException extends Exception {
InvalidAgeException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
void checkAge(int age) throws InvalidAgeException {
if (age < 18) {
throw new InvalidAgeException("Age too low!");
}
}🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: Should custom exceptions extend Exception or RuntimeException?
A: Depends: Exception for checked, RuntimeException for unchecked.
🔄 6. final vs finally vs finalize()
These sound similar but are distinct – a favorite interview topic!
🔍 Comparison Diagram:
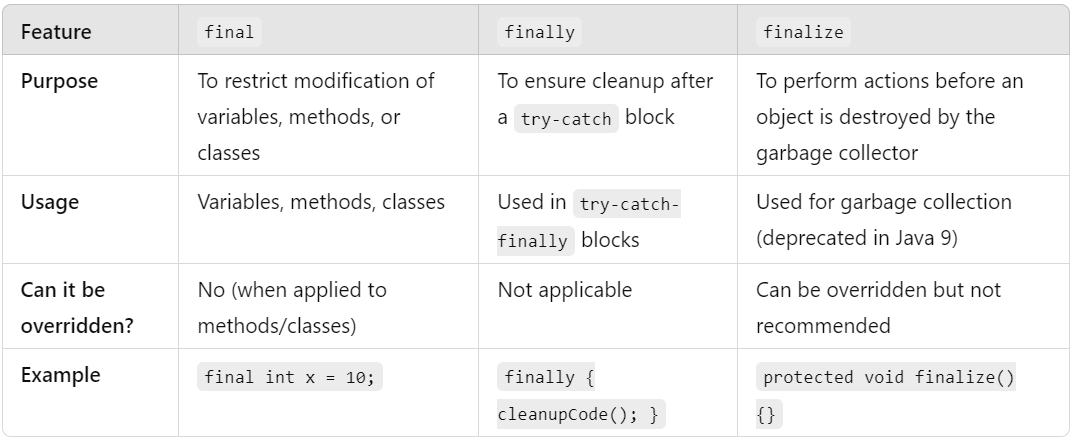
Fallback Text Diagram (if image fails):
final: Locks variables, methods, or classes
finally: Cleanup block after try-catch
finalize(): GC cleanup (deprecated)
🧠 Easy Explanation:
final: Makes things unchangeable (like sealing a contract).finally: Always runs for cleanup (like locking the door).finalize(): Called by GC before object destruction (avoid – deprecated).
| Keyword | Usage | Where | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
final |
Prevent changes | Variables, Methods, Classes | Constants, no override/extend |
finally |
Cleanup | After try-catch | Always runs |
finalize() |
GC cleanup | Method | Deprecated (Java 9+) |
✅ Final Example:
final int MAX_AGE = 100; // Constant
// MAX_AGE = 200; // ❌ Error⚠️ Avoid finalize() – use try-with-resources for cleanup!
🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: Can a final class be extended?
A: No, it’s locked from inheritance.
🔍 7. try-with-resources (Best Practice)
Introduced in Java 7, automatically closes resources implementing AutoCloseable.
🧠 Mnemonic: Like a "self-cleaning" kitchen – resources close themselves.
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file.txt"))) {
// Use br
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} // br auto-closed🤔 Interactive Quiz:
Q: What happens if a resource in try-with-resources throws an exception?
A: It’s still closed, and the exception is caught or propagated.
📝 8. Interview Summary Table
| Concept | Key Notes |
|---|---|
| Throwable | Root: Exception (checked/unchecked), Error |
| Checked Exception | Compile-time; must handle/declare |
| Unchecked | Runtime; optional to handle |
| throw | Manually throw exception |
| throws | Declare in signature |
| finally | Always executes |
| finalize() | GC cleanup (deprecated) |
| try-with-resources | Auto-close resources |
🔥 9. Real Interview Questions & Answers
Commonly asked in companies like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, etc.
Q1: What’s the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions?
A: Checked: Compile-time, must handle/declare (e.g., IOException). Unchecked: Runtime, optional (e.g., NullPointerException).
Q2: Explain the exception hierarchy in Java.
A: Throwable → Exception (Checked: IOException, Unchecked: RuntimeException) & Error (OutOfMemoryError). See hierarchy diagram above.
Q3: Can you have a try block without catch?
A: Yes, with finally or in try-with-resources.
Q4: What happens if an exception isn’t handled?
A: It propagates up the call stack; if unhandled, JVM terminates with stack trace.
Q5: Should you catch Errors?
A: Rarely – they indicate severe issues (e.g., OutOfMemoryError).
Q6: How does try-with-resources work internally?
A: Calls close() in a hidden finally block.
Q7: Explain final vs finally vs finalize.
A: final: Locks variables/methods/classes. finally: Cleanup block. finalize(): Deprecated GC method.
Q8: When to use custom exceptions?
A: For domain-specific errors to improve code clarity.
Q9: Can multiple catch blocks be used? What’s the order?
A: Yes, specific (subclass) to general (superclass) order.
Q10: What is exception propagation?
A: Unhandled exceptions move up the call stack to be handled or crash the program.